[ 產品資訊 ] Optical waveguide metrology and index of refraction mapping
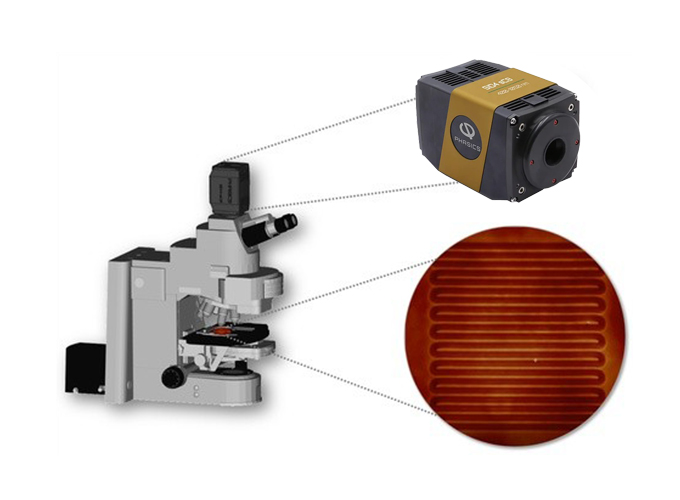
Single-shot mapping of refractive index in waveguides and photonic devices
Optical waveguides are largely used in photonic devices and systems, due to their low optical loss. The refractive index profile distribution of optical waveguides is the key parameter as it determines the insertion losses and propagating modes. Based on its quantitative phase imaging (QPI) technique, Phasics offers high-accuracy metrology instruments for measurement of refractive index variations. Accurate refractive index measurement is necessary for the development, the optimization, and the quality monitoring of produced photonic devices. As a non-destructive method, QPI gives a precise refractive index profile of waveguides. The SID4-Imaging system is adapted for measurements on either optical fiber or laser-written waveguides.
Implementation on any optical microscope
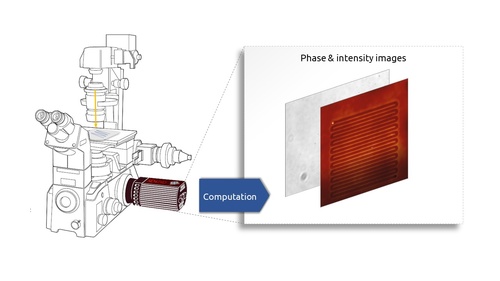
A Phasics quantitative phase imaging (QPI) camera is installed on a classical bright-field microscope. No modification of the microscope is required. Phasics expert software outputs optical path difference (OPD) maps that can be easily converted to a change of refractive index map as follows: OPD = (n2 – n1) x d, with n2 and n1 being the respectives indices of refraction of the surrounding material and the waveguide and d being he thickness of the index change area.
Waveguide measurement setup

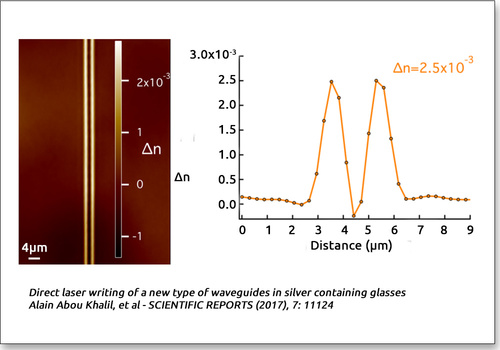
Waveguide imaging can be done in two different configurations: in XY or in the orthogonal plane. Phasics quantitative phase camera measures the optical path difference (OPD) generated by the waveguide. Knowing the mechanical size of the waveguide, it is straighforward to retrieve refractive index values.
OPD (nm) = (n waveguide – n susbtrate) x mechanical thickness (nm)
Waveguide measurement setup (orthogonal)
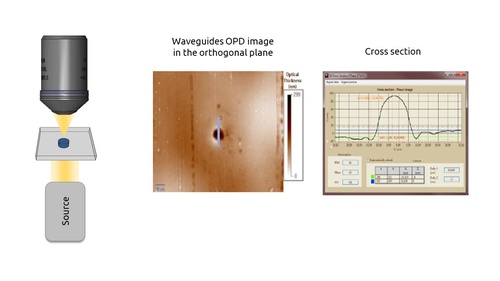
In this representation, the waveguide is sliced and measured in the orthogonal configuration.
Measurement Examples
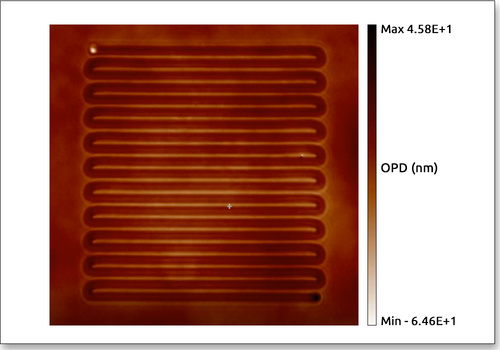
|
|
|
||
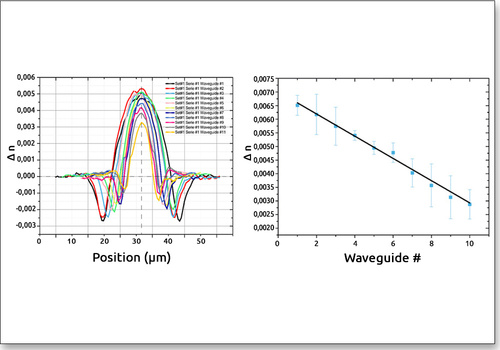
| Optical Path Difference (OPD) map | Changes of refractive index map | Waveguide design validation |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
Related Products

|

|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||