[ 產品資訊 ] Applications of liquid lenses and laser speckle reducers in microscopy

Microscopy
Fast Z focusing and image stability have always been a difficult trade off in the microscopy sector; current technologies such as stepper motor Z actuators or piezo positioners are impacting the throughput in the life science business because of slow speed (stepper motor Z actuators) or because of the small travel and vibration (piezo positioners). It has always been necessary to combine the two different technologies to overcome these bottlenecks, increasing the complexity and the cost of the system.
Optotune focus tunable liquid lenses provide a versatile, compact and cost-effective solution to overcome this challenge. Thanks to the absence of translational mechanics, liquid lenses have the possibility to focus within few milliseconds combining coarse and fine focusing range, ensuring no vibration and reliability with a lifetime of billions of cycles.Optotune focus tunable liquid lenses provide a versatile, compact and cost-effective solution to overcome this challenge. Thanks to the absence of translational mechanics, liquid lenses have the possibility to focus within few milliseconds combining coarse and fine focusing range, ensuring no vibration and reliability with a lifetime of billions of cycles.
A particularly interesting use case is using liquid lenses for z-stacking, to acquire 3D information (DFF) or to compute images with extended depth of field (EDOF).

|

|
| Applications | Advantages |
|
• Wide-field microscopy • Confocal Microscopy • 3D Light Sheet microscopy • Spectroscopy • Digital holographic Microscopy |
• Fast Z stacking • No vibrations • Large working distance range • No chromatic aberrations • Long Life-time (>1B cycles) |

Where to integrate the liquid lens
Non-telecentric configuration
The most straight-forward integration of a liquid lens in a microscopy system is to place it right above the objective lens, which is especially practical for infinity corrected objective lenses. The advantage of this configuration is that very large Z-ranges are achievable. For example, at a magnification of 40x a liquid lens with 5 diopters of tuning range will result in a working distance range of about 160µm. There is a magnification change across the Z-range, which is linear and reproducible.
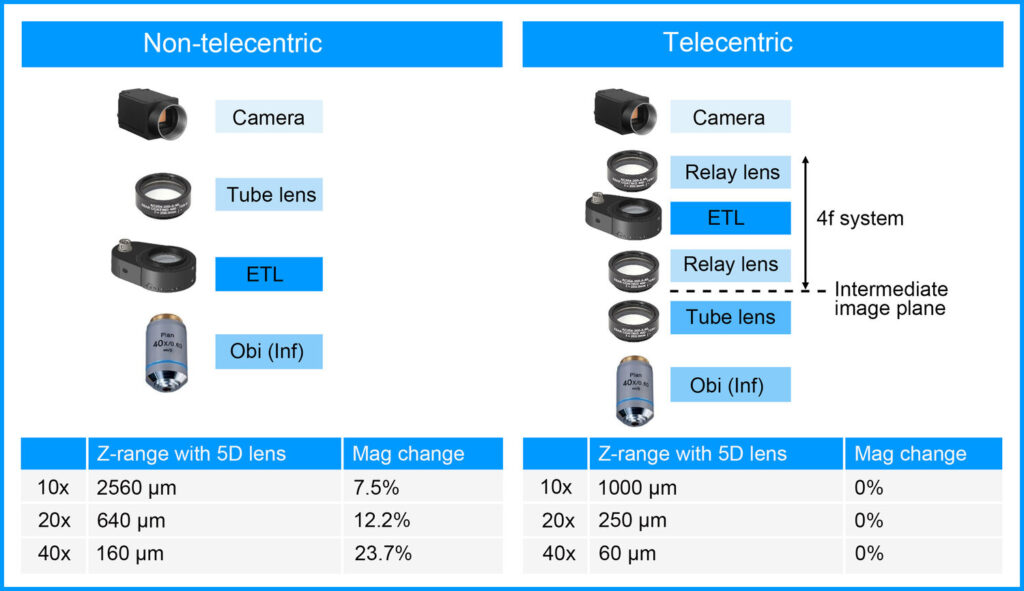
Telecentric configuration without magnification change
Microscopy systems where magnification change is undesirable require a configuration where the liquid lens does not affect the magnification. This is possible by placing it inside a system of relay lenses at a conjugate pupil position. The achievable Z-range is generally smaller as in the non-telecentric configuration.
Speckle-free fluorescence illumination
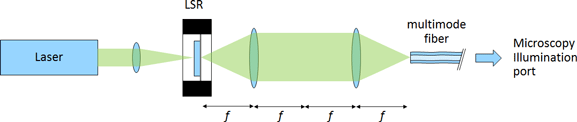
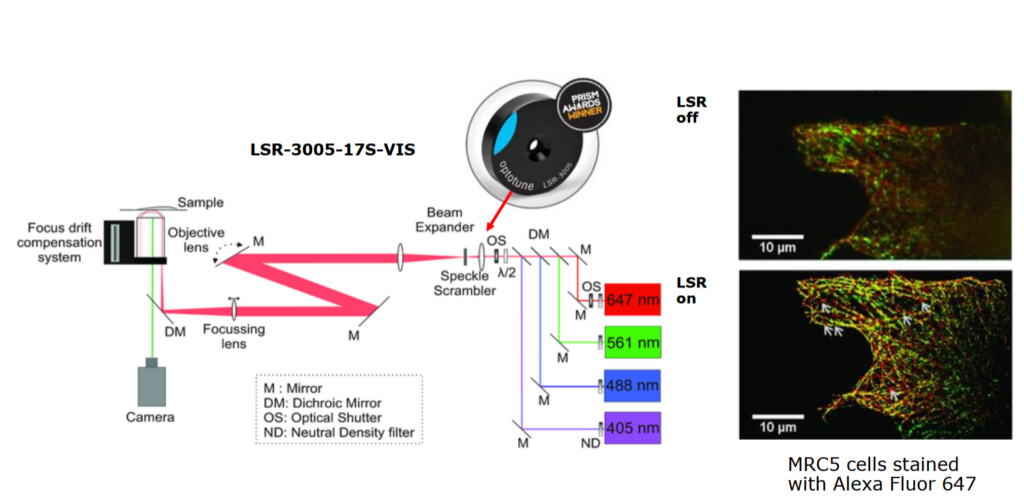
Optotune’s laser speckle reducers can be used to improve the image quality when using lasers for illumination. A typical configuration is to focus the laser onto the oscillating diffuser and image the spot into a multimode fiber via a 4f system.